As the world is leading towards a carbon free environment and transportation has become the major part of the daily rat race, EV’s are becoming more and more popular.
India is becoming the major market of the 21st century, the majority of the car manufacturers are targeting India as their markethub.
Mainly electric vehicles are of three categories :
- Hybrid Electric Vehicles(HEV),
- Plug-in-Hybrid Electric Vehicles(PHEV),
- Battery Electric Vehicles( BEV).
Basically an EV contains a Lithium ion battery which is placed on the floor of the car, keeping the center of gravity very close to the ground, powering the engine. Usually the majority of the EV uses two induction motors, creating rotational motion to both the wheel differentials.

As EVs become more mainstream, the costs are dropping rapidly and there are a wide variety of benefits for drivers making the switch. A completely electric vehicle might cost a quarter or less per mile than a standard gasoline or diesel vehicle.
But as the EV manufacturers are marketing the EV section to be carbon free but actually this is not the actual case. In the USA 80% of the EV owners charge their vehicle from conventional coal power plants.
Reports say that the vision of EV usage in progressing countries has been a failure as majority of the EV cause Carbon emission in either the production period or during the charging phase.
According to another research from the India Energy Storage Alliance (IESA), the Indian EV market would develop at a CAGR of 36% through 2026. Sales of EV has seen an upward rise of 168% in the year of 2021 as the sales in 2021 grew to 3,29,190 from 1,22,607 units.
So the requirement of EV charging stations is expected to grow at a rapid rate.

So, the necessity of on-road charging stations are also going to grow at a rapid rate.
Majority of the EV owners tend to charge the vehicle at their home during the night time but during a busy day the need of charging stations is unparalleled. An average priced, affordable four-wheeler EV in India has an average range of 210km whereas the two-wheelers have around 70km on a single charge.
So the majority of the petrol pumps in India are installing EV charging stations to cater this need. As lastly discussed in Rajya Sabha , dated 02 Dec, 2021 , approximately 22,000 of 70,000 petrol pumps in the country are installing EV charging stations.
But here lies the problem, even though the Government has trying to mandate some portion of these pump stations to adapt to solar power, majority of these EV stations are going to get power from the conventional power stations ,burning much coal and fossil fuels to power these green vehicles, making the entire mission of EV, a failure.
Now to deeply dive into this emerging problem, at first we need to know about the various components and working process of an EV charging station.
Components & Working Process
EV public charging stations use AC type 2 chargers, which are suitable for general application such as petrol pumps, malls, hotels etc. These systems are reliable and long-lasting, and they can be controlled from a single location using centralized management software. EV charging stations installed in public spaces are simple plug-and-play systems that can charge any type 2 car. Through the software that comes with these chargers, the admin may utilize RFID tags for user verification and remotely monitor the apps and energy expenditures.
Various components of a EV charging station are as follows:
- Power source,
- Three-phase electric power,
- Charging points,
- Server with data-base,
- Asynchronous serial controllers,
- Communication TCP/IP ( Transmission Control Protocol/ Internet Protocol) etc.
Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment(EVSE) Technology
EVSE delivers electrical energy from the source to charge the EV’s battery. Not only just charging ,the EVSE system also communicates with the vehicle to ensure that an appropriate and safe flow of electricity is supplied.
EVSE incorporate a number of assemblies and controllers:
- A charging station’s power electronics assembly is its heart. It functions as a power source for the electric vehicle’s inbuilt battery charger. Wires, capacitors, transformers, and other electronic components make up the physical structure.
- The charge controller acts as the charge station’s “street smarts.” It is responsible for fundamental charging operations such as turning on and off chargers, monitoring power use, and storing critical bits of real-time and event data.
- The charge station’s brain is provided by the network controller. It allows administrators to monitor and analyze previous event data by allowing the station to interact with its network (through an on-board telecommunications device). It also uses a set of white (approved) and black (unauthorized) lists to limit user access to charging stations.
- The charge station cable and connector plug into the EV vehicle, these components provide the conduit for a charge to be delivered.
Classification of EVSE Components in Detail
- Physical Components: Internal electronics, controllers,cord,EV-compatible plug and telecommunications devices
- Software: Applications to manage driver access, transparent data sharing , billing and administrative admin access.

Basically the charging station supplies DC electricity ,by using an inverter which is converted into AC charge and then supplied into the vehicle. Here , safety is also a major point as depending upon the usage and charging capability of the EVSE, the safety measures such as Flow monitors , earthing equipment and battery management systems are installed.

- Required Space For EVSE: At any Ev charging station , adequate space must be allocated for vehicle parking and adequate circulation space. The required space for a car parking bay is 5 x 2.5 meters on an average. The Equivalent Automobile Area (ECS) for car parking, including vehicle circulation space, ranges from 23 to 32 square meters, depending on whether it is open parking or underground parking. Exclusive distribution transformers (DTs) are not a universal requirement , and are typically required only in case of high-tension electricity points with multiple charging points. The table below shows the space requirements for DT installations based on the on-site space needs:

Electrical Load & Consumption:
Under AC charging there are 2 categories of charging:
- Normal AC charging: Electric 2-wheelers , 3-wheelers and 4-wheeler vehicles in India have on-board charges that charge at a rate of around 2.5 kW to 3 kW. These AC chargers could charge the vehicles adding around 25 miles of range per hour of charging.
- Fast DC charging: In the present era, in this ever-changing world the requirement of fast charging stations is growing at a rapid rate. Major electric car manufacturers like Tesla, Nissan have on-board chargers with higher power ratings. These 50 amp chargers can add about 37 miles of range in an hour. Currently the available Dc fast chargers in the market require inputs of 480+ volts and 100+ amps (50-60 kW) and can produce a charge of a 100 mile range battery in less than 30 minutes.

- Battery Swapping : As India is a densely populated country and 2 people among 3 Indians have some kind of private transportation in the country, fast charging is not quick enough to cater the future incoming EV charging demand , battery swapping is becoming the most efficient way. In a few states like Chandigarh, Amritsar and Bengaluru ,these swapping machines are getting installed to make the process more fluent. A battery swapping machine usually contains 14 The normal charging stations may have an electrical load of 50 kW and for the heavy duty chargers the average electrical load is 100 kW. Even though the technology is at its preliminary stages, further development and application at a greater stage is further expected.
Problems
- Even though India is trying to reduce the time consumption problem, the existing problem of carbon emission, high tariff charges and usage of fuel-fossils isn’t even thought of.
So, these are the problems the upcoming EV charging sector is going to face:
- More EV, more Carbon ! : As discussed previously, as transportation system starts depending on EVs more and more , carbon emission will increase as the electricity now produced is from fossil fuels,
- Higher Tariff Charges: As tariff charges goes higher and higher ,the electricity cost of various rice mills goes up exponentially,
- Unreliable Power Supply : Even though the public chargers have a battery backup , this backup tends to supply not enough backup time as the demand. The no. of cars used in India is huge,so continuous power supply is more important in this case than the power backup. Major cities like Delhi, Ahmedabad, Bhopal where car density is much higher has a tendency of frequent power cuts which can be problematic for the EV owners.
So, What’s The Way Out ?
Human civilization is increasingly moving toward renewable energy as technology advances. Therefore, the requirement of power is increasing day by day . As conventional power sources fail to cater the need ,renewable energy is entering the power scenario more and more. Moreover, solar plants are the most reliable source of renewable power. We at SunShell Power, offer solar rooftop solutions for every problem in the rice mills. Solar modules have a lifespan of 25 years with minimal maintenance , which makes them super reliable and efficient.
For the solar EV charging stations in gas pumps, we offer two types of rooftop solutions:
- Grid-connected Solar Rooftop Plant,
- Solar Street Light
Grid-connected Solar Rooftop Plant
Solar rooftop power plants that are grid-connected and need low maintenance, as well as a net-metering facility and a credit system based on power banking. If power outages are uncommon and buildings have a large electrical load, this is an ideal power plant.
EV stations need continuous supply of power to keep the charging operation running. These EV chargers have an in-build battery which acts as a backup source.
So, grid-connected power plants are ideal for this situation.

Why On-Grid?
Even though every solar plant is vital to SunShell Power, we strongly advise the government to construct on-grid solar power plants for commercial EV charging stations. We have identified numerous elements that clearly make Grid-connected plants a suitable choice based on our prior experiences:
- Grid-connected power plants has a breakdown percentage of less than 2% which is a very important perk during the busy working days of these charging stations,
- These systems are best suitable when power consumption is high and for cost reduction of electricity bills,
- On-grid systems can be installed with or without net-metering ,
- On-grid solar systems are very cost-effective and easy to install,
- As , breakage rate is minimal ,maintenance is also very minimalistic.

Benefits of Installing Solar
Now you may be asking yourself, “Why should I invest in solar?”
- Solar power plants are a terrific financial and economical investment that is unquestionably a reliable source of power, additionally, it is ecologically friendly and generates green energy.We’ve listed six overall solar benefits based on our research and market demand in India.
- Reduced electricity bills as dependency on conventional electricity is reduced
- Government gives subsidy for solar panel installations,
- Tax benefits by going for accelerated depreciation,
- Low maintenance and long lifespan,
- Environment-friendly solar power is the best way to preserve our planet,
- Reliable power supply to increase the efficiency and operations time of the charging station,
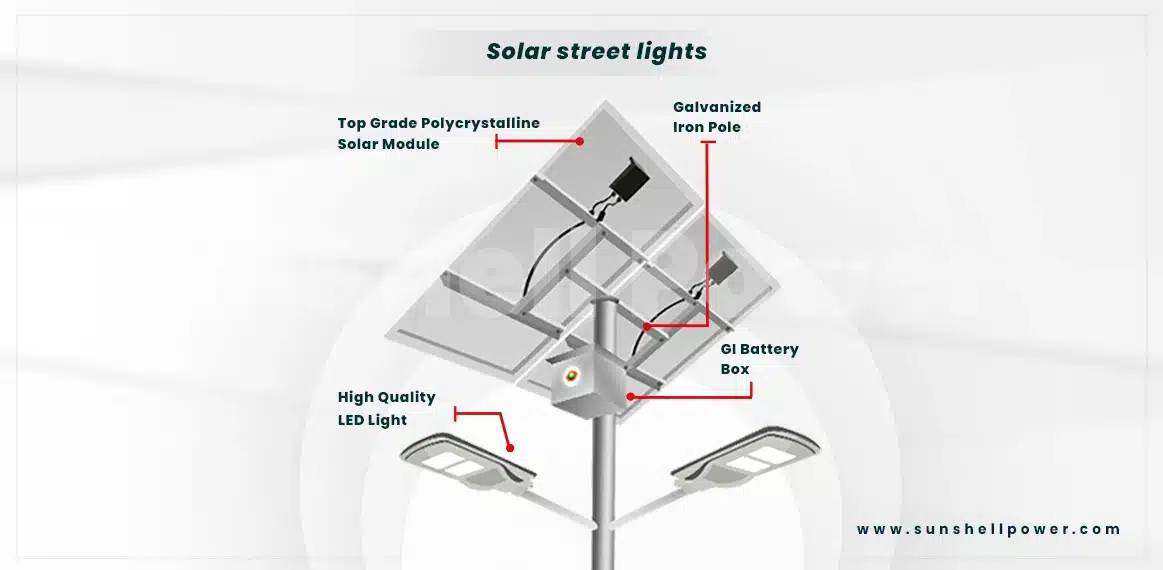
Solar Street Lights
As the compound area of an EV charging station is comparatively big and there will be a no. of cars moving all over the place quite frequently, proper illumination is required in the compound. Solar street lights are the best option in this case as the variants of these lights make the illumination process hassle-free and cost-efficient.
- Two-in-one (semi-integrated) : They’re suitable for different purposes, easy to install and require low maintenance.
- Solar Mini Mast: Best suited for places with unstable power sources, uses green energy and is almost maintenance-free.
Average ROI
The average payback period of a grid-connected solar system in an average EVSE hub with five charging stations , consisting of 10 charging ports is around 3.5-4.5 years. Even though the payback period can change based on the installed charging units and export ports.

Become A Part of The Green Future
As the world moves towards green energy, EV charging stations are adapting to solar as a power source. Various EV stations in Europe and USA are converting into solar. In major states like California 30 EV stations are adapting to solar power and the state government has set a target to solarise at least 30% of total EV stations in between 2025.
In India ,as EV is becoming a growing market day by day new stations must be set up with solar power to achieve the carbon-free transportation target of these electric vehicles.
Enquire Now

