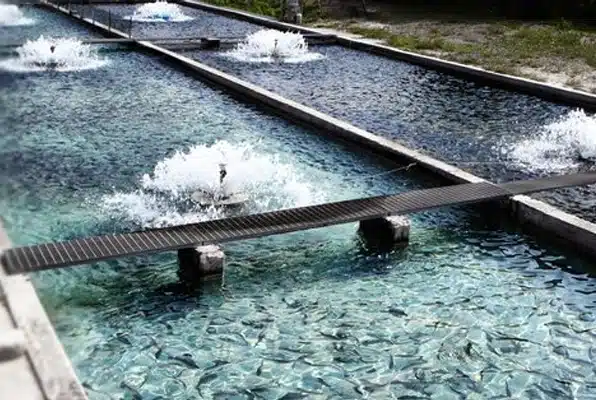
A fish hatchery is a facility for the artificial rearing of animals in their early life stages, especially fish and shellfish. Hatcheries support the aquaculture sector by producing larvae and juveniles of fish, shellfish and crustaceans, which are then transferred to rearing systems such as fish farms. Sometimes they sell the fish eggs to meet market demand.
Indian fisheries and aquaculture are important food production sectors that provide food security, contribute to agricultural exports and employ about 14 million people in various sectors. India’s fish fry industry is the second largest in the world after China’s and contributes about 1.1% to the country’s GDP and 5.15% to agriculture GDP. In 2020, the Indian fish industry will be worth nearly INR 1,232 billion. Between 2021 and 2026, the sector is expected to grow at a CAGR of 10.5% and be worth over INR 2,243 billion.
This huge market demand cannot be met by organic fishing, as these companies produce almost two-thirds of the Indian fish market.
Even though the Indian fish market is very large, certain species of fish are very popular and have a huge demand. Other species such as catfish, murrele and prawns have only recently been introduced into Indian breeding and rearing technologies, including the important main Indian carp species (especially catla, mrigal and rohu). The production rate of the hatchery also depends on the power supply to the facility, as power supply is crucial during the hatching and hatching process, as constant spraying and filtering of water is important during this time to keep the eggs healthy. A number of environmental factors can cause adults to become infertile.
- Components of a fish hatchery: To get to the bottom of this, let’s first look at how a fish hatchery actually works and what components are used in the facility.
A modern Indian fish hatchery usually consists of:
- An Overhead Tank
- Breeding Tank,
- Hatching Tank,
- Nursery Tank ,
- Filter Tank,
- Submersible Pump for water reservoir (1 HP),
- Surface pump for water filtration and sprinkler(1-2 HP),
Work process of a Fish Hatchery
- Collecting fish: First, the fish are collected from the fishery market for artificial rearing and growth and the bellies of the fish are examined. If the belly of the fish is soft, it means that the fish is mature and ready to spawn. These fish are then sent back to the market for immediate sale, while the rest are set aside for further processing and taken to the breeding tank.
- Collecting and fertilising the eggs: The stunned fish are taken to the egg-laying room, where they’re first separated by sex. The eggs and sperm are collected by hand, mixed with water and kept in a bucket to initiate fertilisation while the excess sperm, ovarian fluid and blood are flushed away.
- Fertility sampling: 10 hours after fertilisation, fertility samples are taken and examined to check the blastodisc of an egg, which indicates the success of fertilisation,
- Rotation and sufficient oxygenation: The eggs are then transferred to the gross tank where the water is continuously circulated using a surface pump and an external sprinkler repeatedly sprays water into the tank to provide sufficient oxygen for the eggs to hatch. This process is continued for about 1 month until the eggs have hatched.
- Feeding the fry: When the fry hatch from the incubators, they’re kept in the same water for 9 days without being fed, because during this time they absorb liquid from the same larval water. They’re then released into the fresh water and fed before release. The quality and specification of the water is determined according to the needs of the fish.
- Growth of the fish: The larvae are thoroughly examined and their daily growth is monitored. After a certain period of time or depending on the needs of the market, these fish are taken to the market for sale and some of the higher quality fish are kept for further fertilisation.
Throughout the larval rearing phase, aeration is crucial for maintaining an adequate concentration of dissolved oxygen in the water, maintaining an even water temperature throughout the water column by turbulence and reducing the ammonia content in the water.
This aeration can be done with a root fan or an air compressor.
Although it may seem that the changeover in this industry is going without a hitch, in reality this isn’t the case.
Problems faced by Fish Hatchery:
Even though fish hatcheries solve a major food supply problem, this industry faces some problems:
- Higher DG costs: since most fish hatcheries use a DG engine to keep the process going, costs keep rising. A 20 kW engine DG consumes an average of 7.264 l of diesel for one hour of operation.
- Unreliable power supply: Although some of the hatcheries are connected to the electricity grid, the power supply is unreliable, with frequent power cuts in the rural areas where the hatcheries are located.
- Low quality feeding: In India, it’s been found that the fish that are farmed here aren’t of high quality. This is due to poor quality and inadequate feeding. The engines of DG consume a large part of the farm capital, which further deteriorates the quality of the fish and leads to lower revenues.
- Damage the environment: Fish farms can transmit diseases and parasites to migrating fish if they aren’t operated properly. In particular, during the hatching or hatching process of the eggs, when the oxygen supply is cut off, the eggs are destroyed and emit toxic gases.
- Carbon emission: As most hatcheries use DG engines, an average of 188.64 kg of CO2 is emitted every day, further fuelling global warming.
To find an affordable, efficient and reliable solution, we need to know what the electrical load of an average Indian fish hatchery is.
Electrical load
The electrical load of a fish hatchery depends on the size and production of the facility. Below you’ll find a table showing the electricity consumption and expenditure for the machines and pumps used:

On average, the electricity consumption of a fish hatchery is 22.5 kWh per day, although the figures may vary depending on productivity, size and working hours.
Emergency Power Backup
Even though most hatcheries run on diesel engines, some of them use a mains connection as the main power source and DG engines as backup.
Oxygenation
The main component of fish growth is oxygenation where oxygen needs to be circulated every moment, as oxygenation is what the growth of fish depends on.
Normally, the alternate solution in this oxygenation is the use of Oxygen Tablets. But this is not an optimal solution as regular use of Oxygen tablets leads to abnormal growth of the fish and makes the water more polluted. Hydrogen Peroxide which is a bleaching agent, could cause skin issues and gil damage of the fishes as well as bleaching the eggs, making the hatching process more difficult and inefficient.
Only a few known scientific studies on the effects of hydrogen peroxide on fish and overall water quality have been conducted, and as a result, the exact concentration at which hydrogen peroxide becomes toxic to fish is largely unknown – as with most things, the few studies that have been done have concluded that it varies greatly depending on the fish species and overall water parameters where aeration increases the level of dissolved oxygen.in order for the natural biological activities of a pond system to remain balanced It also aids in the movement of water in low-circulation zones (which might otherwise accumulate unwanted amounts of algae) and promotes chemical treatment mixing throughout the pond.
As the process is fully biological, there are no side-effects to the health and growth of the fish. Studies show that 250-500 ppm of Hydrogen Peroxide at 75℉ is required for eggs to hatch.
The second drawback which’s the increasing pollution level in the water can be catered by usage of mechanical aerators. As regular oxygen flow in water maintains the filtration process of water.
In a brick-lined pond of size ( 26’ x12’x6’) has seen an increase of 2095 kg/acre of more fish with an approximate benefit of Rs.144,130 when mechanical aeration is used for 6 months in the hatchery during a peak breeding season.
So what’s the way out? Solar Solutions Fish Hatchery!!
Human civilisation is increasingly moving towards renewable energy as technology advances. Among the renewable energy sources, solar panels are the most reliable source of power. At SunShell Power, we offer a rooftop solar solution for every problem for cold storage of any capacity and type.
Solar panels have a lifespan of 25 years with minimal maintenance, making it a reliable source of power.
We offer four types of solar solutions for cold stores:
1. Grid-connected solar rooftop and ground-mounted systems,
2. Solar rooftop with backup,
3. Solar submersible pump,
4. Solar surface pump.
Solar Rooftop and Ground-mounted systems:
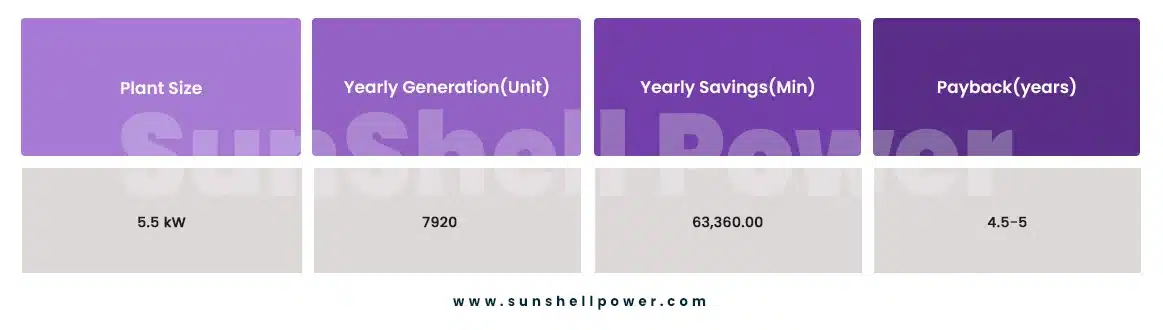
- Grid-connected solar systems: reliable and efficient grid-connected solar power plants with minimal maintenance and the possibility of net-metering, a credit system by baking electricity. For existing fish hatcheries, this is the optimal solution. For a fish hatchery with an average consumption of 20 kWh, we recommend a grid-connected system with a size of 5.5 kW, consisting of 17 modules with 335 watts.
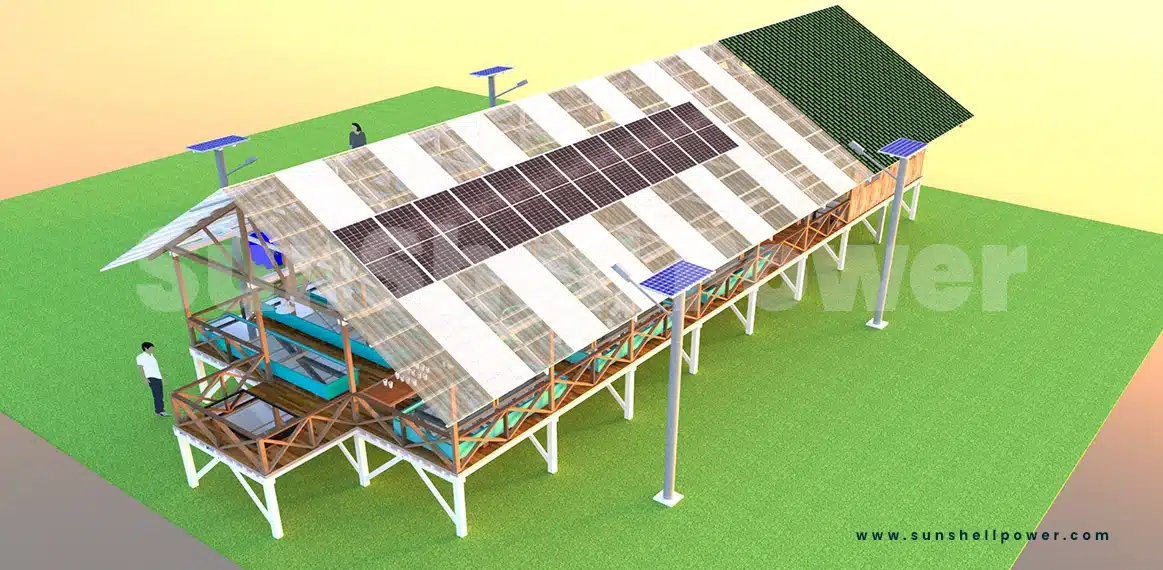

Why grid-connected?
These systems are best suited when electricity consumption is very high and you want to reduce your electricity bill,
- Lack of dependence on a reliable power source,
Grid-connected systems can be installed with or without grid feed-in and are also a source of income in themselves, - Grid-connected solar systems are very cost-effective and easy to install,
- Grid-connected systems are maintenance-free, which makes them effortless to maintain.
Benefits of installing solar power plants
Now you might be asking yourself, why should I invest in a solar system?
Apart from being environmentally friendly and producing green energy, solar power plants are a great financial and economic investment that also provides a reliable source of energy. Based on feedback from our previous customers, here are 6 general benefits of solar power systems:
- Hedging against rising energy costs,
- Scalable design for easy upgrades,
- Scalable design for easy upgrades,
- RPO compliance ,
- Self-reliance,
- Green commitment ,
- Carbon neutrality ,
- The government gives subsidies for the installation of solar panels.
Average ROI
The average payback period of a solar system in a fish hatchery is 4.5-5 years. However, the payback period may vary depending on the production rate and size of the fish hatchery.
Submersible solar pump
These solar-powered pumps are submerged in the water below the ground. They’re used to pump water from underground. Most fish aquacultures use this type of pump for water supply. There are different pumps with different capacities depending on the requirements of the consumer. For new and upcoming fish farms, it’s best to use this type of pumps for underground water supply as the first step should be towards a green world with added benefits of the product.

Advantages
- less dependence on grid connected power,
- 5 year warranty (normal submersible pumps have only 1 year warranty),
- Zero maintenance and a breakage rate of less than 5%,
- A step towards a green future.
Solar surface pump
Surface pumps are used to pump surface water from sources such as springs, ponds, tanks or shade wells, etc.
These pumps can be used in water supply and irrigation systems. Since these solar pumps are self-priming, they can distribute water over a large area.
There are also different types of surface pumps to cover all needs.
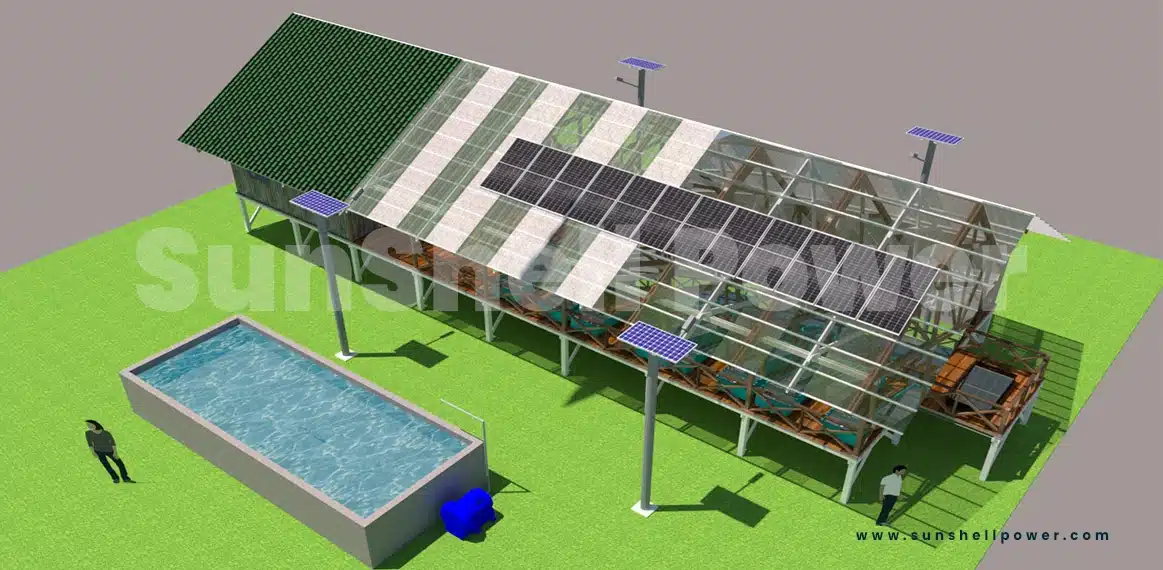

Advantages
- no fuel costs – as it uses free sunlight,
- long operating time,
- Very reliable and durable with a breakage rate of less than 3%,
- easy to operate and maintain,
- environmentally friendly with a tilt towards a green earth.
Payback
The average payback time of a solar surface pump is 5-6 years.
Alternative solutions
Hybrid solar: Since most of India’s fish hatcheries are located in rural areas where power outages are common, the installation of a hybrid solar system is highly recommended as the backup battery reduces the dependency of the system on the motors DG and hence the emission of carbon into the environment.
Off-grid
Since hybrid systems are costly and may exceed the initial investment budget of many farms to install a solar system with a buffer battery, the next best option is an off-grid system. In case of frequent power outages, such systems would help keep the hatchery running for a few more hours.
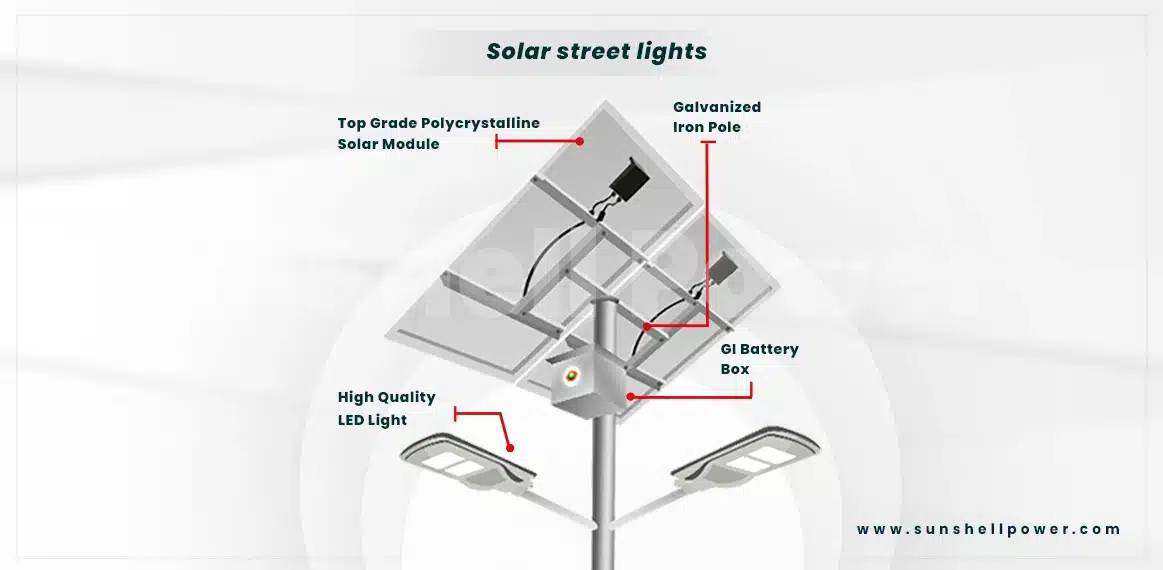
Solar street lighting
In India, fish farms raise valuable fish like salmon, catfish, cod and others. Recent incidents like the theft of fish worth Rs. 12 lakh in Valamangalam in May 2020 have raised questions about the security of the facility. Solar street lights are the best thing that can be done to enhance and improve the security of the site through reliable lighting technology.
There are three types of solar lights:
All-in-one solar street light
Compact, lightweight design with motion sensor that can be used anywhere.
Two-in-one (semi-integrated).
They can be used for different purposes, are easy to install and require little maintenance.
Solar mini mast
Best suited for places with unstable power sources, uses green energy and is almost maintenance-free.
Advantages of Solar Solutions for Fish Hatchery
Now you may be asking yourself why I should invest in solar energy?
Apart from being environmentally friendly and producing green energy, solar energy is a great financial and economic investment, as well as being a reliable source of energy.
Based on feedback from our customers, we’ve compiled 8 general benefits of going solar:
- lower electricity bills as dependence on conventional energy is reduced,
- lower bills for running emergency generators DG,
- government subsidies for installation of solar pumps as per KUSUM C YOJNA (pumps below 7.5 HP),
- tax benefits through accelerated depreciation,
- easy availability of credit at low interest rates for installation of solar panels ,
- Environmentally friendly solar energy is the best way to preserve our planet.
Enquire Now

