As the world evolves toward a more contemporary and technologically sophisticated way of life, the increasing likelihood of complex illnesses and pandemics becomes more feasible.
The global market for oxygen filling sector is expected to reach USD 14.15 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 6.9 %. The COVID 19 epidemic has generated an immediate global demand for oxygen, and the situation is the same in India. In the year 2020, the market was valued at USD 2971.40 million.

Medical professionals often employ medical oxygen gas cylinders for therapeutic and diagnostic reasons. Medical oxygen gas systems, such as oxygen concentrators and compressed oxygen gas cylinders, are widely used in homecare settings, and are often preferred by elderly patients who have mobility issues and need a consistent oxygen supply.
As during the pandemic time the oxygen demand hit a jump of 600%, demand for such stations is rising day by day. During the pandemic, the situation became so terrible that the government was forced to redirect oxygen from steel mills to hospitals.
The Government of India has made an approach to establish in-house oxygen production plants to cater to the demand.As of the last report from November,2021 the daily production of oxygen is around 1,750 metric tons.
In addition over 550 cities and districts along India were geo-mapped & an online system was established that tracks the movement of a commodity in real time.
Some authorities like DRDO, MInistry of Health Sector of Bihar, Gujarat have targeted to make 500 & 75 oxygen plants respectively in 6 months.
Now, to dive deep into this oxygen producing scenario, let us first know how artificially and industrially oxygen is produced.
Components & Working Process of Oxygen Factories:
Separation of air using either a cryogenic distillation process or a vacuum swing adsorption technique is the most popular commercial method for creating oxygen. By liquefying air at very low temperatures (-300°F), cryogenic distillation separates oxygen from air. Ambient air is compressed in many steps with inter-stage cooling before being cooled further with chilled water.

Now, let’s check out how step by step oxygen is being made.
- First the air is being filtered by an air filter to remove dust particles then passed to a compressor, where there are two valves: an inlet valve and a discharge valve. The inlet valve sucks the air in and through use of a piston the air is compressed into high pressure. The compressed air discharged through the discharge valve.
- When air is being compressed it heats up, so after air is compressed the outlet pipe is passed through a cold chamber ,where by the use of liquid Nitrogen(temperature < -196℃) it cools down to a temperature of -200℃. Now the compressed air is sent to the separator. Here CO2 is separated from the air as in the form of dry ice.
- Now as the air is free of CO2, it travels to the expansion turbine where the air is allowed to expand and it turns into a liquid form , called liquid air. In the end it is sent to an air distillation column where it is gradually warmed up. Due to the temperature rise Nitrogen is separated first at -196℃ , after that comes Argon which evaporates at -186℃.The Oxygen boils at a temperature of 182-183℃.Thus Oxygen which has a higher boiling point (-185℃) is left in the liquified form which is then removed through a pipeline from the chamber.
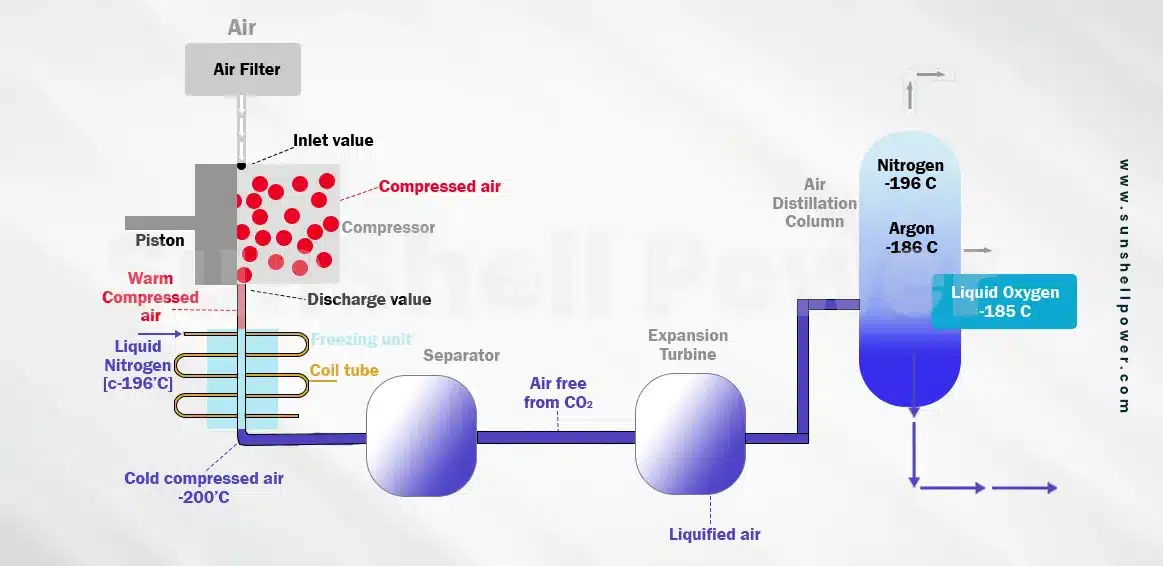
- The Argon gas, filtered from here, is sold separately for industrial use, especially for welding purposes. Nitrogen gas( N2) is also sold separately for making fertilizers and in the food-packaging industry.
Oxygen Storage:
After the liquid Oxygen is filtered, it is transported in special containers. The amount of pressure at which Oxygen is stored in a container is around 3000PSI / 200 Bar.
The regular oxygen cylinders come with a flow-meter, which controls the outlet pressure of the Oxygen. A normal patient in hospital needs OXygen at a pressure of 50 PSI. The cryogenic tanks have a capacity of 3,016 to 61,620 liters.
These tanks are called cryogenic because the term Cryogenic means anything which is stored below the temperature of -150 ℃ to the absolute zero( -273.16℃).
Electrical Load:
Now as we know about the industrial production process Oxygen, we may look into the required electrical load for these filling plants. To produce 1 liter of Oxygen on an average 0.0165 unit electricity is required.
The following table shows the required electricity usage to produce Oxygen Cylinders of different sizes.
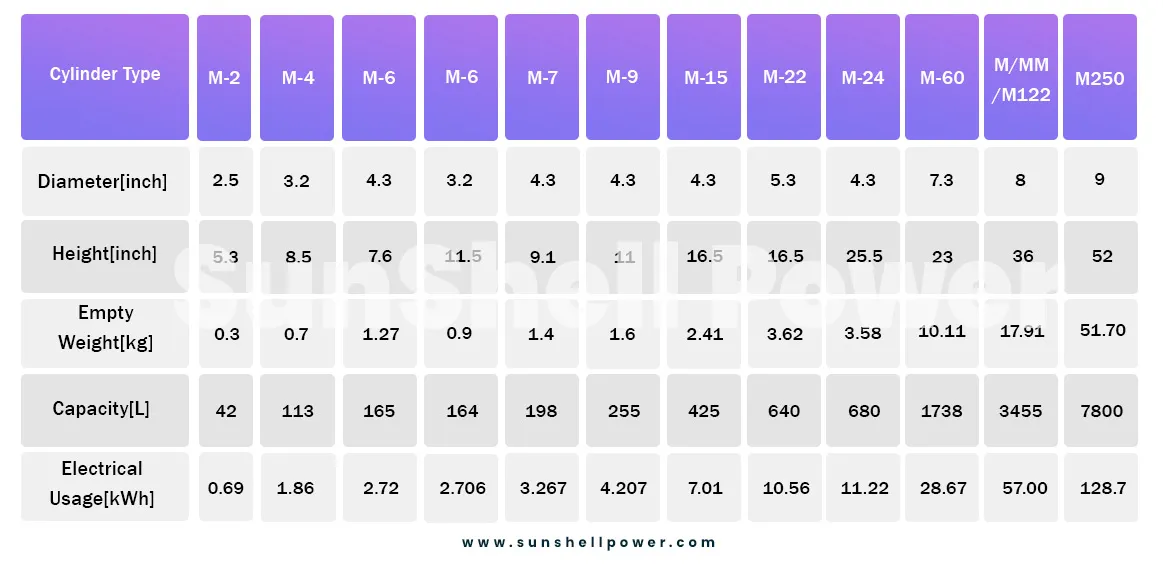
** The capacity of the cylinders are measured in a constant pressure of 1200 psi **
The shown electrical consumption can vary as per the purity of the Oxygen separated from the air.
The electrical load of such an Oxygen filling facility depends on the storage capacity of the plant. The Government of India has strict guidelines for Oxygen storage and usage. For a storage room with one-hour fire-rated walls and doors with 45-minute fire-rated, then the allowed storage capacity is 3,000 cubic feet of O2, maintaining a safe distance between the Oxygen cylinders and any combustible materials in the room.
To produce this much Oxygen 1,401.6816 units of electricity is needed.
If such an Oxygen plant with Expansion Turbine Method, the plant of this capacity will require a Grid-connected plant of 350 kWp.
Even though the numbers can change based on the production and storage capacity.
Oxygen Purity : According to the ASME code, Indian Pharmacopoeia Oxygen must have a purity percentage of at least 93%. As new and modern methods are implemented for Oxygen production costs of more pure Oxygen are going higher and higher.
Power Backup
Majority of the Oxygen plants in India use DG motors as their backup power source.
Problems faced by Oxygen Factories
During the COVID 19 2nd wave, the commercial oxygen production sector had serious issues; nonetheless, the industry now faces a large future demand and the prospect of additional biological pandemics like the COVID.Even if the profit margins are relatively high, major challenges such as exponential price rises, lack of permanent infrastructural development, monopoly in the power supply category, and increase in tariff charges have become roadblocks in the evolution of this firm.
As mentioned above, the Govt. of India are trying to cater these rising issues by building in-house Oxygen manufacturing units in the hospitals, there are quite a few no. of problems:
- Ever-rising Tariff Charges: As tariff charges go higher and higher, the electricity cost of various health sectors increases drastically. According to the Government’s approach as these plants will be attached to the healthcare facility, the facility will have to bear more electricity cost.
- More Carbon, More Pollution: As this sector uses grid-energy, reliable source of energy emits a lot of carbon in our environment, further turning our green planet into gray. Quite to be precise, to produce 1kWh of electricity, 0.95 kg of carbon is emitted.
- High Diesel Cost: The Ministry of Healthcare have a guideline of backup energy storage for 96 days for any department in the health facility campus, further increasing the operational cost.
- Power Outage In The Sector: The Central Government of India has rigorous guidelines for allowed downtime each year in health facilities. Because the manufacturing plant will not be classified as an emergency, power failures such as the summer power loss in 2020 will have a significant impact on Oxygen production.
So, What’s The Way Out? Solar Solutions Oxygen Factories!!
Human civilization is increasingly moving toward renewable energy as technology advances. Solar power plants are also the most dependable renewable energy source. SunShell Power provides solar rooftop solutions for any health-related issues. Solar modules have a 25-year lifetime and need little maintenance, making the plant a stable power source.
For such Oxygen filling stations, we offer three types of solar solutions:
- Grid-connected Solar Rooftop Plant
- Hybrid Solar Plant,
- Off-grid Plant.

Grid-Connected Solar Rooftop Plant (On-Grid):
Reliable and efficient grid-connected solar power plant with minimalistic maintenance and available net-metering facility, a credit system through banking of power. If power cuts are not frequent, it is the best solution for such Oxygen filling stations.
Power Plants With Storage Facility:
- Hybrid Solar Power Plant: As Oxygen supply is an essential service, reliable power supply is one of the most crucial items here. This occurs as a result of load changes induced by changing demand in steel factory equipment. Hybrid power plants are the best option in these situations since the backup battery decreases the facility’s reliance on DG backup motors, lowering carbon emissions. However, since the needed load in hospitals and health facilities are substantially larger, even higher-quality batteries with enormous storage capacity are suggested.
- Off-Grid Solar Power Plant: Hybrid plants are expensive, and many facilities’ initial investment budgets for a solar plant with backup may be exceeded by hybrid plants. Off-grid plants are the greatest alternative. The use of such would assist keep health facilities operational for a few extra hours in the event of frequent power outages.
Why On-Grid?
Even though in SunShell Power, every solar plant is important and valuable, for Oxygen plants in hospital facilities, we highly suggest authorities to install on-grid solar power plants. From our previous experiences, we have pointed out several points which clearly makes Grid-connected plants an ideal choice:
- These systems are best suitable when power consumption is high, and one needs to reduce the electricity bills,
- On-grid systems can be installed, with or without net-metering,
- On-grid solar systems are very cost-effective and easy to install,
- As there is no battery backup, maintenance is minimal, which can be helpful in the busy environment of the hospital.

Benefits Of Solar Solutions Oxygen Factories:
Now, the question may arise to your mind – “Why should I invest in solar ?”
Solar power plants are a terrific financial and economical investment that is unquestionably a dependable source of electricity, in addition to being environmentally beneficial and creating green energy.
We’ve compiled a list of eight overall advantages of installing solar rooftop power plants based on feedback from prior customers.
- Reduced electricity costs as dependency on conventional electricity are reduced,
- Reduced bills on running back DG sets,
- The government gives subsidies for solar panel installations,
- Tax benefits by going for accelerated depreciation,
- Easy availability of loans at low interest rates for solar panel installations,
- Low maintenance and long life-span,
- Environment-friendly solar power is the best way to preserve our planet,
- Proper utilization of the unused space on the rooftop,
- NREL found that, among other health benefits,solar power results in fewer cases of chronic bronchitis,respiratory and cardiovascular problems, and lost workdays related to health issues. As these plants are going to be installed in the hospital premises, health issues are going to be a major concern.
Solar Submersible Pump:
As water is one of the most important elements in producing Oxygen, reliable and constant supply of water is essential. Solar submersible pumps are the best option to deliver water in a constant flow from underground for both toilet and cooling purposes.
Solar Street Light:
As storage and maintenance of tanks is as important as the production process, proper safety is required in the storage compound as Oxygen is an OXidizer gas i.e. it causes other materials to burn.
- Two in one (Semi-integrated): Used for a variety of purposes, these are easy to install and are low-maintenance.
- Solar Mini Mast: Best for places with unstable power sources, uses green energy and needs almost zero maintenance.
Average ROI
The average ROI of a grid-connected solar plant in an Oxygen filling station is around 3.5-4.5 years, although it can change based on the load of the health facility.

Reliable Power, Reliable Service:
In India, during the COVID-19 second wave, supply of Oxygen was one of the major issues. Even though in some of the areas production wasn’t the problem, storage and filing of Oxygen was the reason behind this crisis. Keeping the exact pressure in those tanks and keeping the desired temperature is a challenge. As solar power plants are a reliable source of energy, it is the best power source to cater any upcoming Oxygen crisis in the country.
The Government of India has taken steps to plant mini Oxygen facilities in the rural areas. Solar plants are also the best option where grid facility is not available.
Enquire Now

